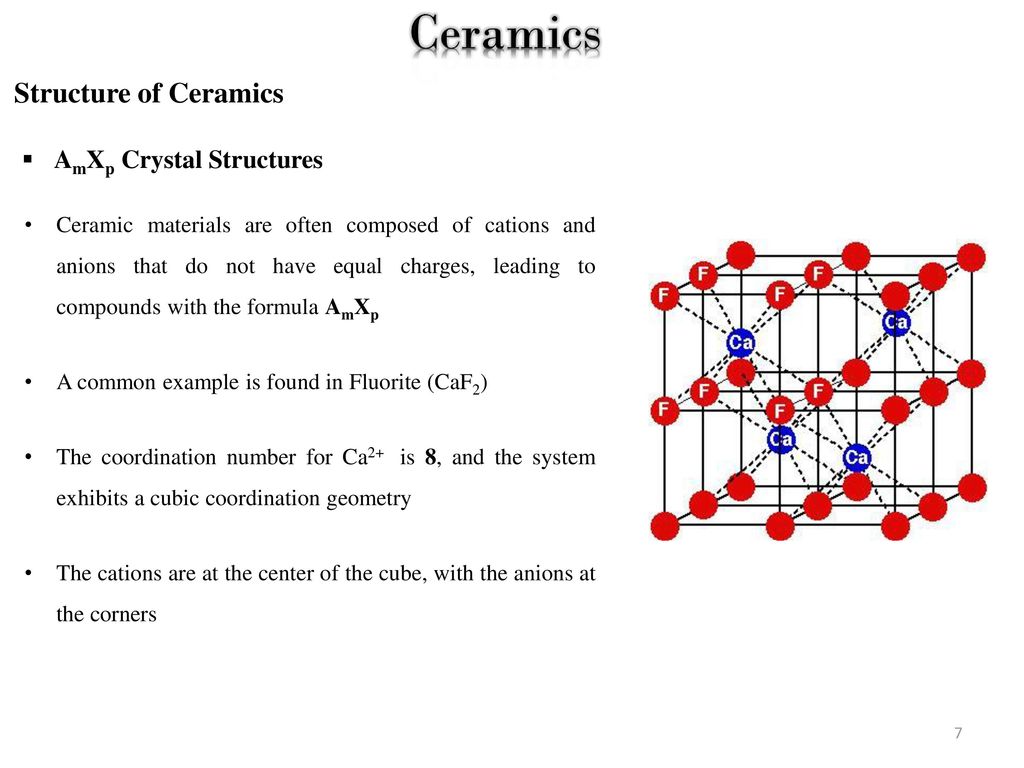
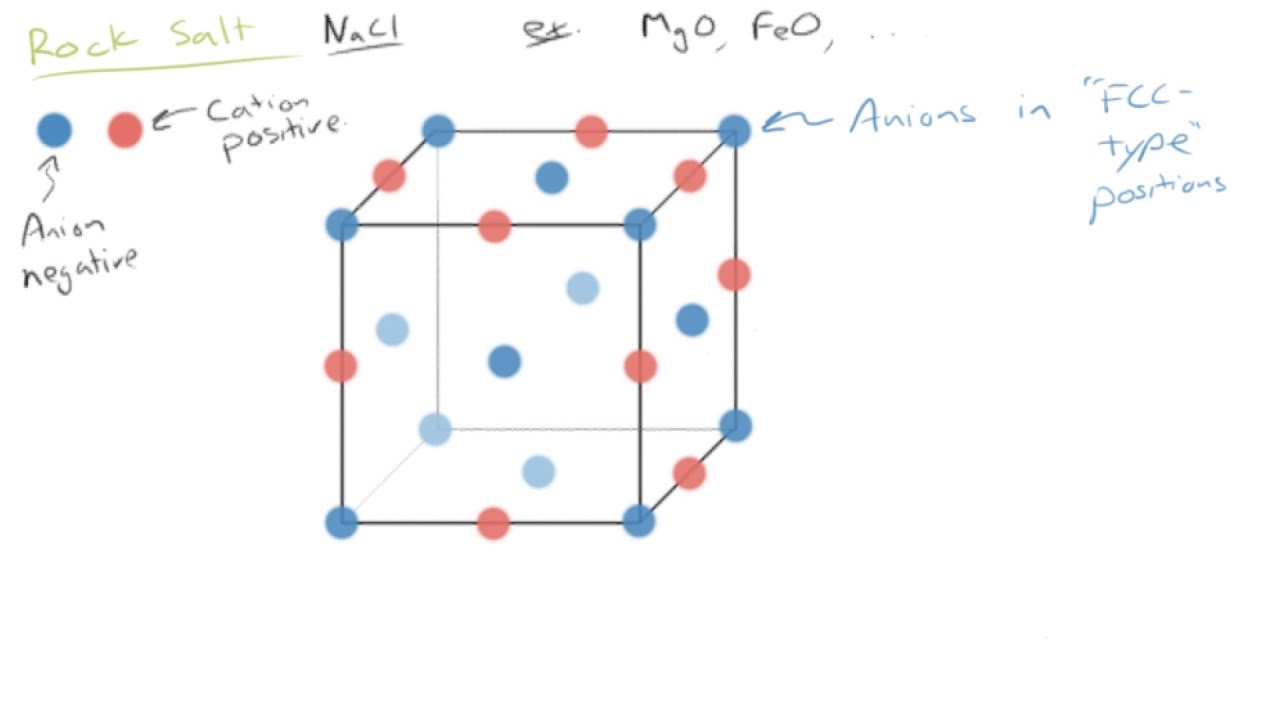
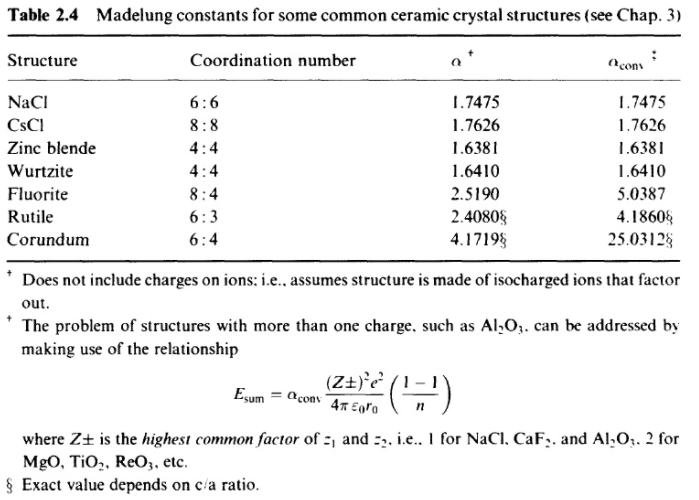
Common Ceramic Crystal Structures

Ceramic and glass components.
Common ceramic crystal structures. For example while ceramics are perceived as electrical and thermal insulators ceramic oxide initially based on y ba cu o is the basis for high temperature superconductivity. Industrial ceramics are commonly understood to be all industrially used materials that are inorganic nonmetallic solids. 2 ceramic structures continue factors influence crystal structure magnitude of electrical charge of ions relative size of ions non metal metal ions rc ra 1 äcations must be next to anions maximize of nearest neighbors that are anions ästable structure anions and cations must contact each other äthe of anions depends on ratio of rc ra. Ceramic composition and properties atomic and molecular nature of ceramic materials and their resulting characteristics and performance in industrial applications.
It is derived from the greek word πιέζειν. Just like in every material the properties of ceramics are determined by the types of atoms present the types of bonding between the atoms and the way the atoms are packed together. However it should be noted that the crystal structures of ceramics are many and varied and this results in a very wide range of properties. Whereas monocrystalline materials are grown as.
Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of three dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in the material that constitutes this. Fe ni al called cations and non metallic ions e g. O n cl called anions bonding will usually have some covalent character but is usually mostly ionic.
Piezoelectricity is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials such as crystals certain ceramics and biological matter such as bone dna and various proteins in response to applied mechanical stress the word piezoelectricity means electricity resulting from pressure and latent heat. Structures of ceramics outline introduction crystal structures ceramic structure ax type crystal structures amxp type ambnxp type silicate ceramics carbon ceramic structures two or more different elements more complex than metal structures ionic and or covalent bonds a mix of ionic and covalent bonds. Common ceramic crystal structures structure name structure type anion packing co ordination anion example no. Piezein which means to squeeze or.
Since these structures are most common they will be discussed in. Usually they are metal oxides that is compounds of metallic elements and oxygen but many ceramics. Different types of crystal unit cell structures or lattices are found in nature. In crystallography crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms ions or molecules in a crystalline material.