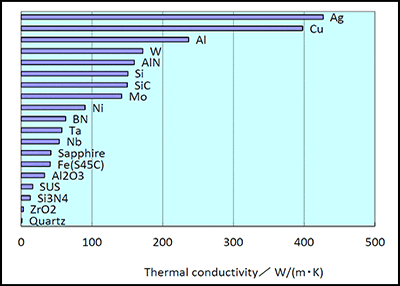
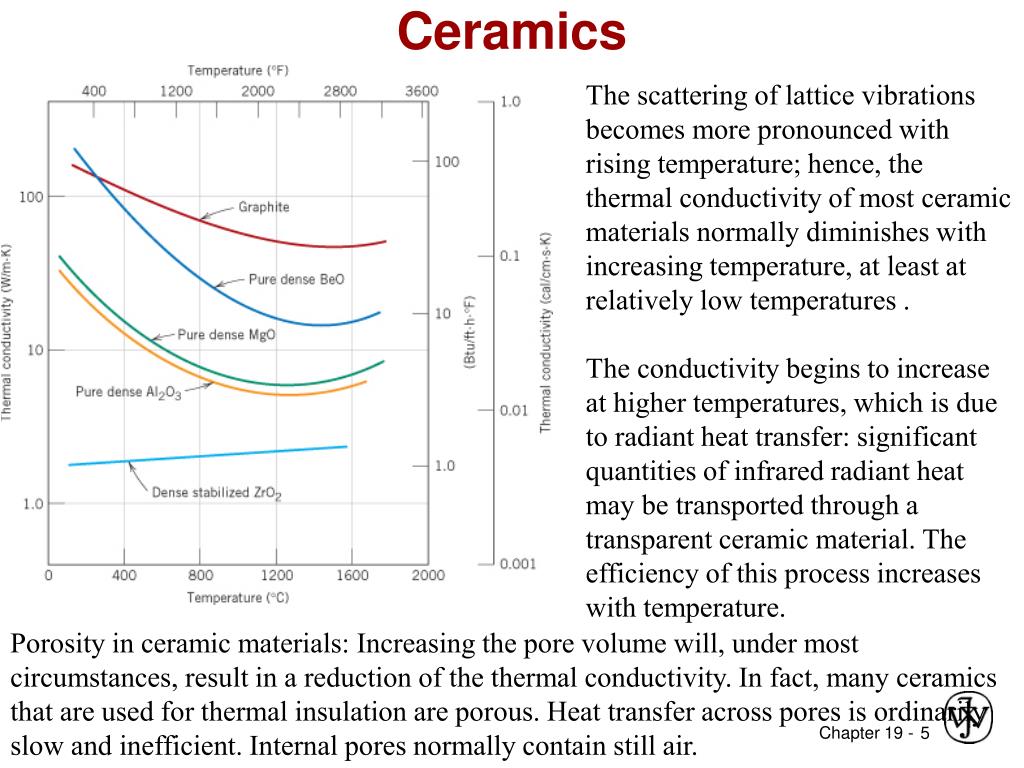
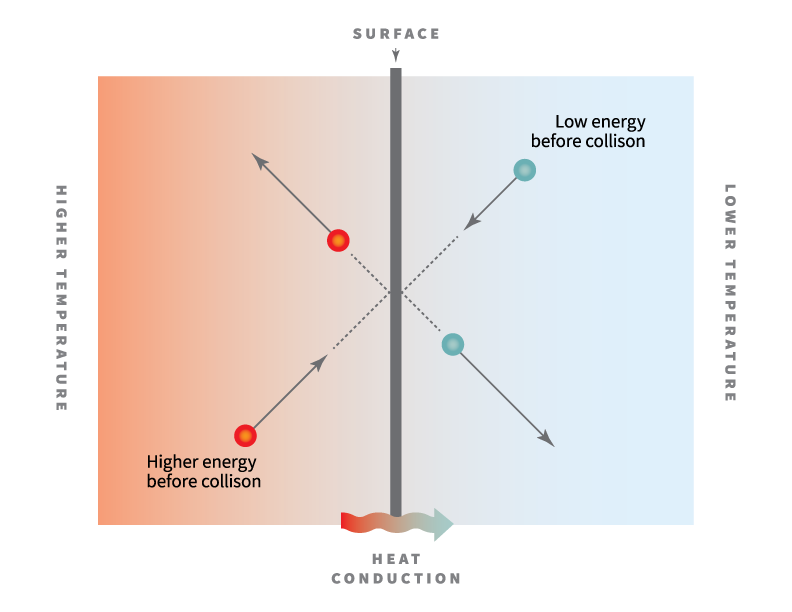
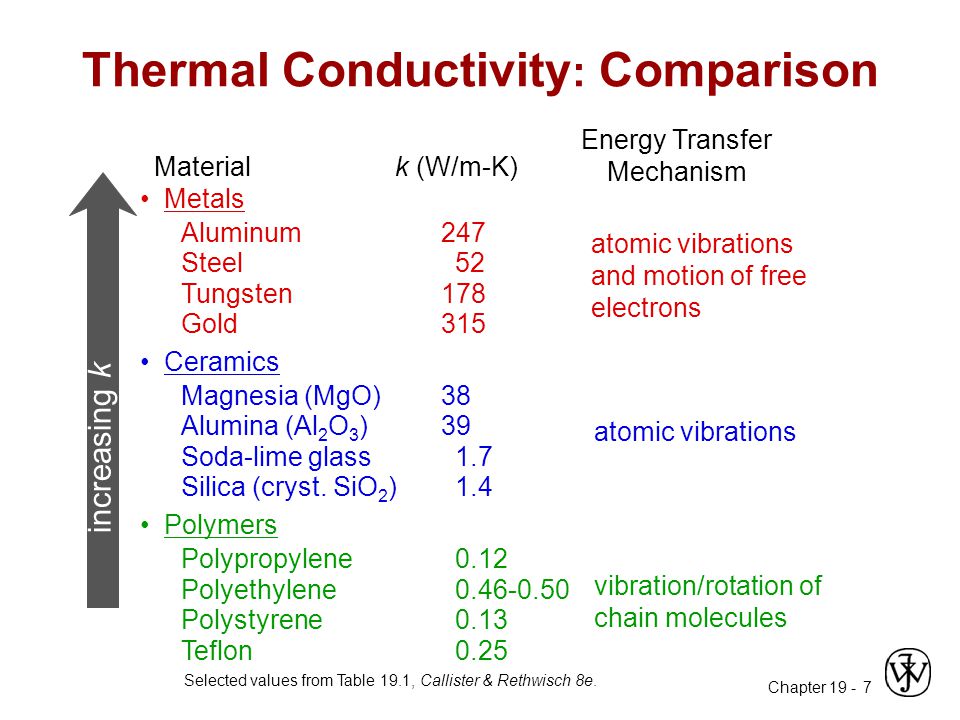
Conductivity Of A Metal And Ceramic With Increasing Temperature

This results in increase in resistance of metal and hence decrease in conductivity.
Conductivity of a metal and ceramic with increasing temperature. In a certain range increasing the thermal conductivity of ceramic materials by specific methods will improve its ability of heat conduction heat convection and heat radiation so as to further expand its application field. Thermal conductivity of liquids decreases with increasing temperature as the liquid expands and the molecules move apart. The law named after german physicist georg ohm appeared in 1827 in a published paper laying out how current and voltage are measured via electrical circuits. In electrolytic conductors the ions are charge carriers and with increase in temperature ionization increases and hence conductivity increases.
Thermal conductivity a transport property frequently referred to as λ is a measurement of the ability of a material to conduct heat considered to equate to the time rate of heat flow under steady conditions through unit area per unit temperature gradient in the direction perpendicular to the area. Taylor found that the thermal conductivity k t of the transition metal carbides and nitrides increases with increasing temperature t at high temperatures this behavior is different from that of metals for which k t is approximately independent of t as noted by taylor it is proposed that defects cause the electron thermal conductivity of the carbides and nitrides to increase with. With many assumptions including. When temperature increases the vibration of metal ions increases.
With the increase in temperature the electrical resistance of metals increases the reason of which is increased vibrations of atoms at high temperatures which in turn leads to increased collisions between the vibrating atoms and moving electrons.