Conductivity Of Ceramics Depend On

These effects depend on filler content lying in the range of percolation threshold which may cause the increase in crystallinity and conductivity of composite.
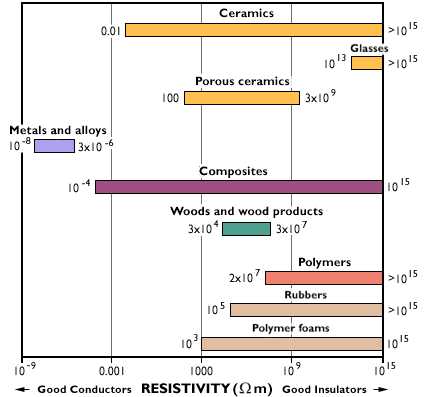
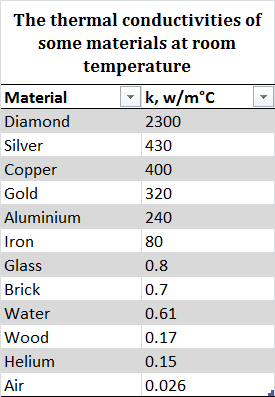
Conductivity of ceramics depend on. In ceramics the ionic bonds holding the atoms together do not allow for free electrons. However the scatter in the thermal conductivity bulk density data in certain studies particularly when data from industrially processed brick are involved suggests that thermal conductivity depends apart from porosity on other characteristics such as phase composition microstructure humidity or the presence of soluble salts. When high temperatures are. 7 82 mn 427 ag j smk for metals and 1 10 pyrex glass 2310 diamond j smk for ceramics.
Electric conductivity in ceramics as in most materials is of two types. Indeed many ceramics are quite conductive electrically. Correspondingly there are numerous factors affecting the electron mobility in nanocomposite or composite systems to enhance the electrical conductivity of materials. The atoms of metal elements are characterized by the presence of valence electrons which are electrons in the outer shell of an atom that are free to move about.
Electrical conductivity in metals is a result of the movement of electrically charged particles. Conductivity of a material depends on its temperature density and moisture content. The thermal conductivity normally found in tables is the value valid for normal room temperature. Electrical conductivity of polymer graphite composites depends on the formation of percolation network while it depends on parameters of filler i e electrical conductivity aspect ratio surface energy loading value distribution dispersion and orientation matrix i e electrical conductivity surface energy and polymer structure.
According to smith et al. To return to the example of diamond this material though considered to be a ceramic has a thermal conductivity higher than that of copper a property the jeweler uses to differentiate between true diamond and simulants such as cubic zirconia a single crystal form of zirconium dioxide. Fortunately many measured thermal conductivities of metals and ceramics are available. The transmission of either type of wave phonon or photon is.
This value will not differ much between 273 and 343 k 0 70 c. Although the thermal conductivity is affected by faults or defects in the crystal structure the insulating properties of ceramics essentially depend on microscopic imperfections.