Cooling Rate Ceramics Vs Metals

The melt strength of a polymer increases with increasing molecular weight and it can withstand a higher thermal gradient.
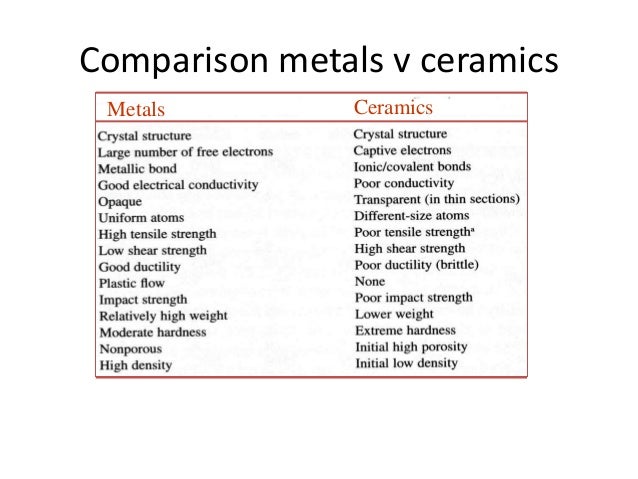
Cooling rate ceramics vs metals. This plateau corresponds to the formation of a metastable massive transformation 9 or a martensitic transformation product. The cooling rate depends on the melt strength and wall thickness. When gradually cooled there are a few nuclei formed and the grain boundary is large. Ceramics are intermediate in density between polymers lower and metals higher in the range of 2 6 gms cm3.
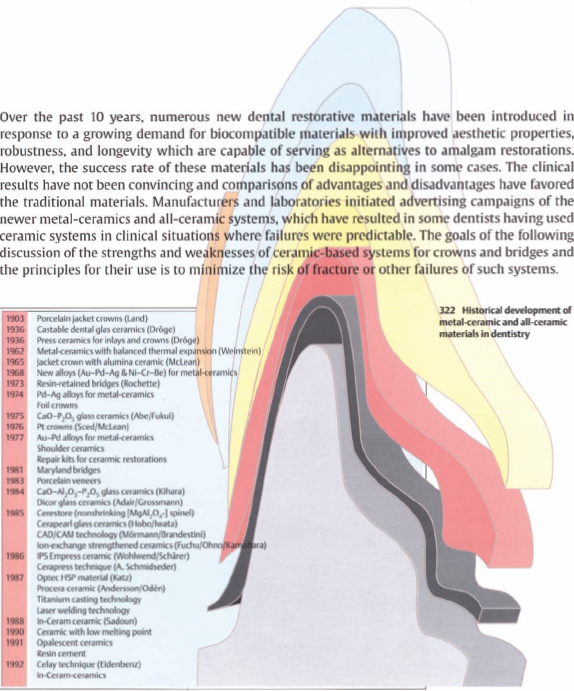
Generally large billets 150 and 300 kg in table 10 5 should be cooled at rates between 8 and 15 c h down to 250 c. This slow cooling rate allows the. The above figure shows the effect of cooling rate taking the case of steel. While some crucible types support metal temperatures encompassing a broad spectrum of metals it often is necessary to select crucibles targeted to specific metals or alloys and with more limited operating temperature ranges.
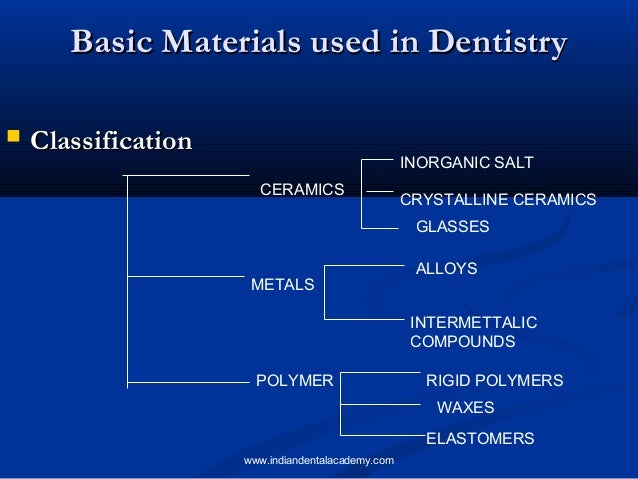
Ceramic lcte tm mass properties include things like density. Yes crystalline yes free roaming valence electrons tied up in bonds. Diagram for each alloy. 4 cooling rate and cooling mode.
2 5 8 the transformation start temperature becomes independent of the cooling rate i e a plateau forms in the t t t. Good electrical conductivity poor insulator good thermal conductivity poor. The general principle for the development of reasonable sintering conditions is to burn high quality porcelain technical indicators such as performance in the most economical way see economic indicators. Above a certain critical cooling rate ccr 200 c s for several ti cu alloys as shown in fig.
High tensile strength low. Metallic type of bonding ionic covalent. Now we are ready to calculate the rate of heat transfer by substitution of known values into the above equation. 2 highest sintering temperature.
When steel is heate. Low shear strength high. But still i am not sure that it is possible to apply by means of a dilatometer a constant cooling rate of 2500 k s on a standard steel sample d 10 mm l 3 mm from 900 to 300 c using helium or. When cooled rapidly nuclei formed are more grain size is more.
Opaque optical properties transparent. Compositions with several allotropes such as sio2 will have minor differences in density. Taken together as a group these metals represent a temperature range from 400 c 750 f to 1600 c 2912 f.